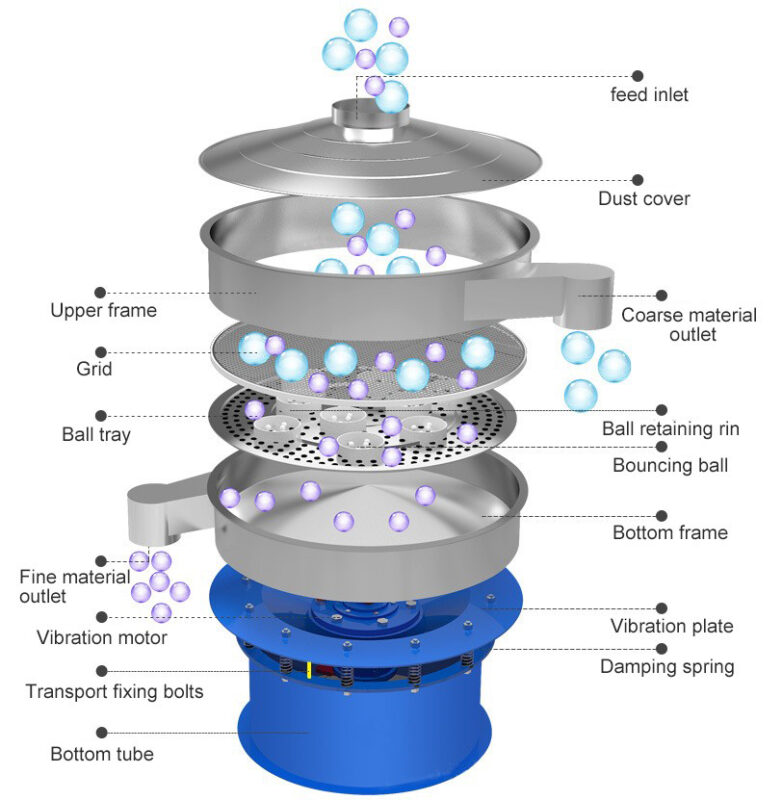
Basic Components and Their Functions
In industrial processes, the Vibrating Screen Sieve Analysis Process is fundamental for determining particle size distribution within granular materials. This method employs a vibrating screen to segregate particles based on size, ensuring quality control and process optimization.
Central to this process are the Basic Components and Their Functions:
- Vibration Motor: Generates the necessary vibratory force, propelling particles across the screen mesh.
- Screen Frame: Provides structural support, maintaining the integrity and alignment of the screen mesh.
- Screen Mesh: Acts as the filtering medium, with apertures allowing particles of specified sizes to pass through.
- Bouncing Balls: Positioned beneath the screen mesh, these components prevent clogging by dislodging trapped particles.
- Base Bracket: Ensures stability, anchoring the entire assembly during operation.
During operation, the vibration motor imparts oscillatory motion to the screen frame, causing particles to stratify. Smaller particles navigate through the mesh apertures, while larger ones remain atop, facilitating effective separation. This meticulous classification is vital across sectors such as mining, pharmaceuticals, and food processing, where particle size directly influences product quality and performance.
Operational Steps and Best Practices
The Vibrating Screen Sieve Analysis Process is a pivotal technique in material classification, enabling precise determination of particle size distribution within a granular sample. This method is indispensable across various industries, including mining, pharmaceuticals, and food processing, where particle size critically influences product quality and process efficiency.
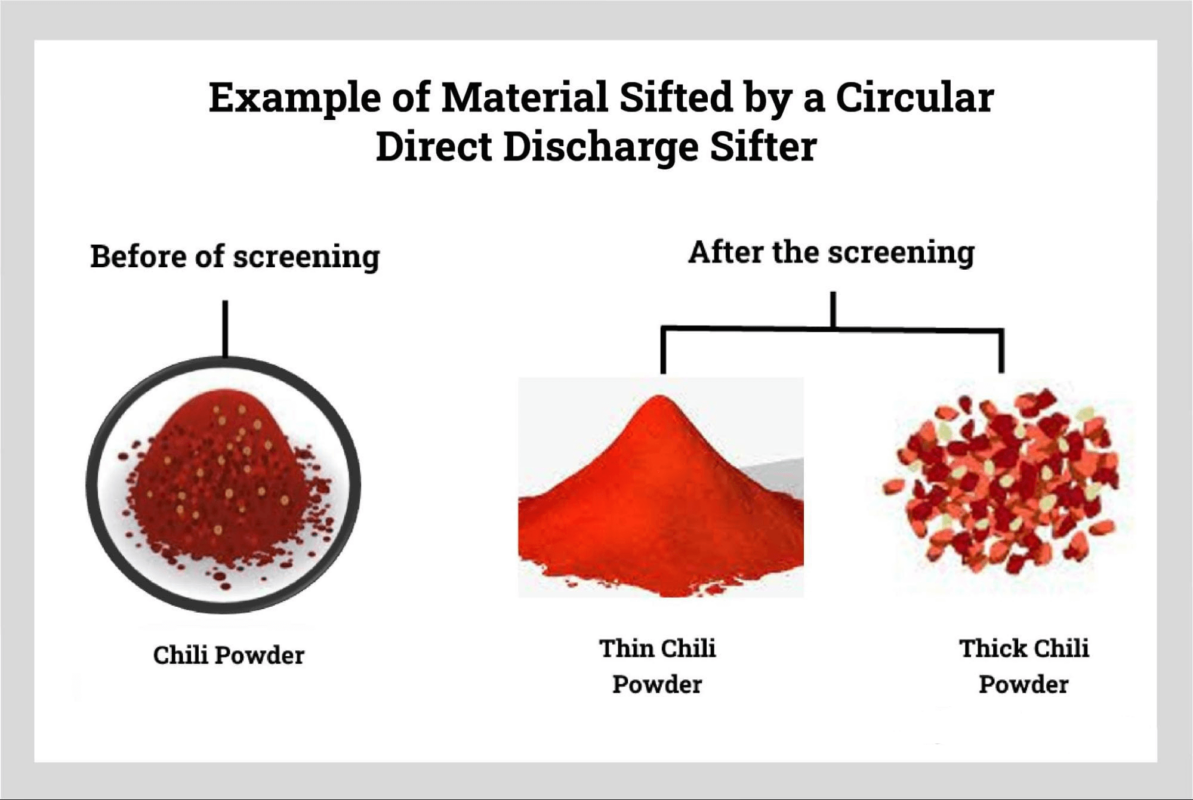
Operational Steps and Best Practices
- Sample Preparation: Begin by obtaining a representative sample of the material. Ensuring the sample accurately reflects the bulk material is crucial for reliable results.
- Selection of Sieves: Choose sieves with appropriate mesh sizes that align with the desired particle size range. The selection should conform to standardized specifications to maintain consistency.
- Assembly of the Sieve Stack: Arrange the sieves in descending order, with the largest mesh size at the top. Secure the stack firmly to prevent displacement during the process.
- Setting Up the Vibrating Screen: Place the assembled sieve stack onto the vibrating screen apparatus. Ensure that the machine is calibrated correctly, with settings adjusted to suit the material’s characteristics and the analysis objectives.
- Conducting the Sieving Process: Activate the vibrating screen to initiate the sieving. The vibratory motion facilitates the stratification of particles, promoting efficient separation.
- Duration of Sieving: Maintain the operation for a standardized duration to ensure completeness. Over-sieving or under-sieving can lead to inaccurate data.
- Weighing and Recording: After sieving, carefully remove each sieve and weigh the retained material. Document the mass corresponding to each sieve meticulously.
- Data Analysis: Calculate the percentage of the total sample retained on each sieve. Construct a particle size distribution curve to visualize and interpret the results effectively.

Best Practices
- Regular Equipment Maintenance: Conduct routine inspections and maintenance of the vibrating screen and sieves to ensure consistent performance and longevity.
- Avoid Overloading Sieves: Introduce an appropriate quantity of material to prevent sieve overloading, which can compromise separation efficiency and accuracy.
- Consistent Sieving Time: Standardize the sieving duration for similar materials to enhance reproducibility and reliability of results.
- Proper Cleaning Procedures: Thoroughly clean sieves after each use to prevent cross-contamination and maintain measurement integrity.
By adhering to these Operational Steps and Best Practices, professionals can achieve accurate and reproducible results in particle size analysis, thereby enhancing quality control and optimizing industrial processes.